Geometry is a fascinating realm of mathematics, filled with intriguing concepts and angles that shape our understanding of space and form. In this article, we embark on an in-depth exploration of acute angles, covering their definition, degree measurement, visual representations, mathematical formulas, practical examples, properties within triangles, real-world applications, and the crucial distinctions between acute and obtuse angles.
Table of Contents
Acute Angle Definition:
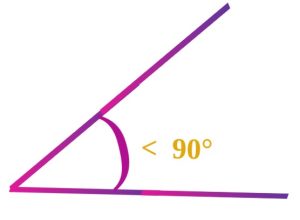
An acute angle is an angle that measures less than 90 degrees. In other words, it is an angle whose magnitude is smaller than a right angle. For example, an angle measuring 20 degrees, 75 degrees, or 89 degrees would all be acute angles.
Acute Angle Degree:
The measure of an acute angle is always less than 90 degrees. The degree measure of an acute angle could be any value between 0 and 90 degrees, exclusive.
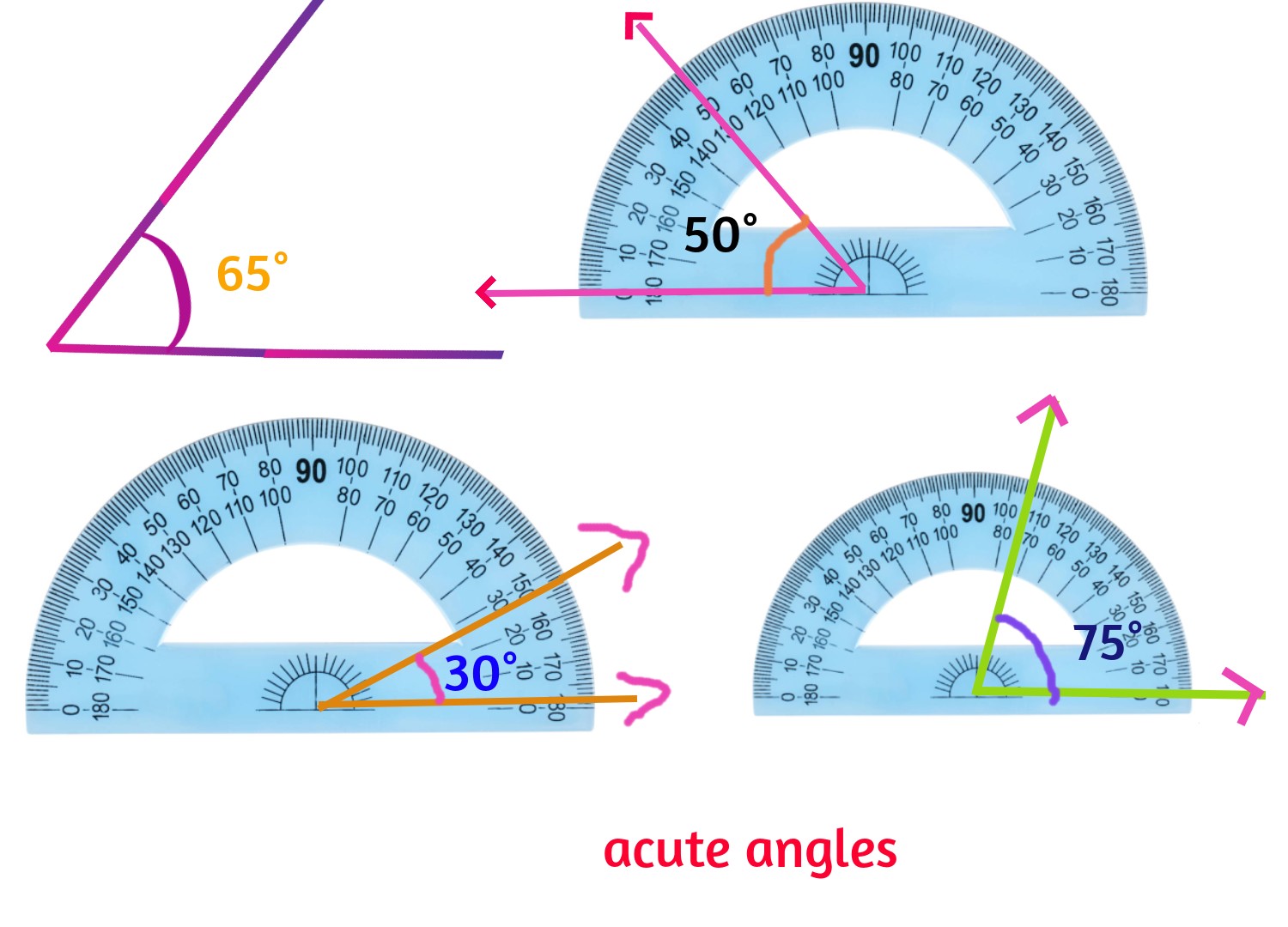
Acute Angle Images:
Acute Angle Formula:
In the context of an acute triangle, the relationships among the lengths of its sides are governed by the following conditions:
- The sum of the squares of the two shorter sides, denoted as a and b, is greater than the square of the longest side c: a2 + b2 > c2
. - The sum of the squares of the second shortest side, b, and the longest side, c, is greater than the square of the shortest side, a: b2 + c2 > a2
. - The sum of the squares of the shortest side, a, and the second longest side, c, is greater than the square of the remaining side, b: c2 + a2 > b2
Acute Angle Examples:
Examples of acute angles could include:
- A 30-degree angle.
- A 60-degree angle.
- Any angle with a measure between 0 and 90 degrees.
Acute Angle Triangle:
An acute-angled triangle is a triangle in which all three angles are acute angles, meaning each angle is less than 90 degrees.
Properties of Acute Triangle:
-
- Properties of an acute triangle include:
- All three angles are acute.
- The sum of the interior angles is less than 180 degrees.
- No angle is a right angle or obtuse angle.
- Properties of an acute triangle include:
Acute Angle vs Obtuse Angle
| Characteristic | Acute Angle | Obtuse Angle |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An angle that measures greater than 0 degrees | An angle that measures greater than 90 degrees |
| Measure Range | Between 0 degrees and less than 90 degrees | Between 90 degrees and less than 180 degrees |
| Symbolic Representation | ∠ABC, where the measure of ∠ABC < 90 degrees | ∠PQR, where the measure of ∠PQR > 90 degrees |
| Examples | 30 degrees, 45 degrees, 60 degrees | 100 degrees, 120 degrees, 150 degrees |
| Triangle Classification | All angles in an acute-angled triangle are acute | One angle in an obtuse-angled triangle is obtuse |
| Trigonometric Functions | Trigonometric functions are defined for acute angles | Trigonometric functions are defined for obtuse angles |