Exponents, also known as powers or indices, are mathematical notation that represents repeated multiplication of a number by itself. They play a fundamental role in mathematics and are denoted by a superscript number. Here’s an introduction to exponents!!
Table of Contents
What are Exponents?
Exponents, also known as powers or indices, are mathematical notations used to represent repeated multiplication of a number by itself. They simplify the expression of large numbers or repeated operations and play a crucial role in various mathematical concepts. The basic notation for exponents is written as an, where a is the base and n is the exponent.
Here’s a breakdown of key concepts related to exponents:
- Base: The base is the number that is multiplied by itself. In an, a is the base
- Exponent: The exponent indicates the number of times the base is multiplied by itself. In an , n is the exponent. Example: In 23 ,2 i s the base, and 3 is the exponent. It means 2 × 2 × 2.
- Expression: An expression with an exponent represents the repeated multiplication of the base. Example: In 34,means 3 × 3 × 3 x 3.
- Exponent Rules
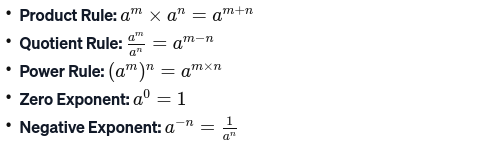
Types of Exponents
Exponents can be classified into different types based on their properties and applications. Here are some common types of exponents:
Whole Number Exponents:
These are the most basic type of exponents where the exponent is a positive whole number.
Zero Exponent:
When an exponent is zero, the result is always 1.
Fractional or Rational Exponents:
Exponents can be fractions or rational numbers. They indicate taking roots.
Negative Exponents:
Negative exponents indicate taking the reciprocal of the base raised to the positive exponent.
Integer Exponents:
Exponents can be positive, zero, or negative integers.
Variable Exponents:
Exponents can also be variables, often denoted by letters like x or y.
What are Negative Powers?
Negative powers are a specific type of exponent where the exponent is a negative integer. When a base is raised to a negative exponent, it indicates taking the reciprocal (or finding the multiplicative inverse) of the base raised to the absolute value of the exponent.
The general form of a negative power is:
![]()
Here, a is the base, and n is a positive integer.
